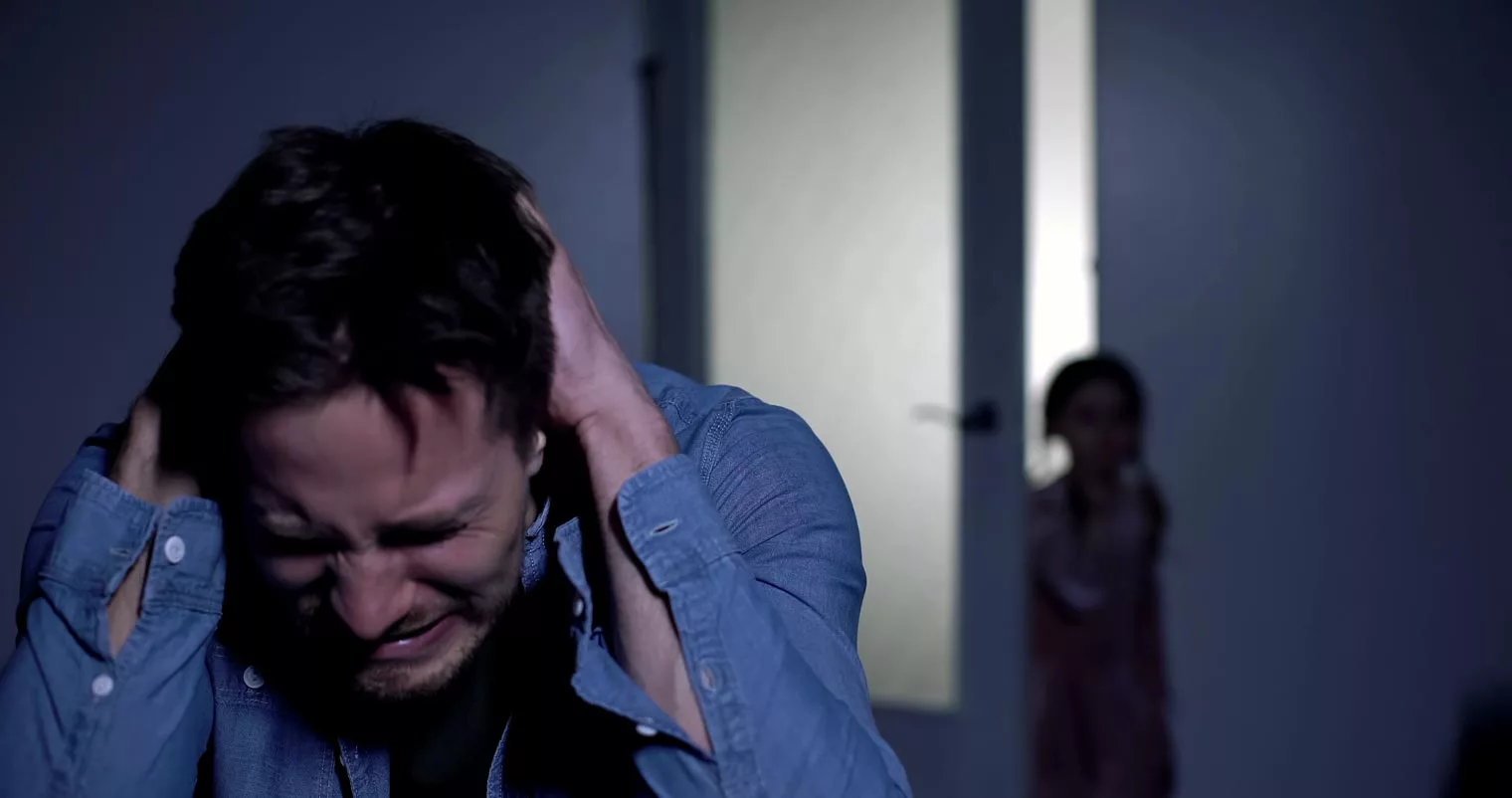
CPTSD vs PTSD
Differences Between PTSD and C PTSD
Many people have some understanding of PTSD, but not so many know what CPTSD is. In this article, we look at exactly what both of these mental issues are, and why the treatment of Complex PTSD is increasingly sought after across the United States.
If you have either of these mental health conditions, keep reading to learn more about CPTSD vs PTSD, and how to find effective help for both conditions with Icarus Behavioral Health in New Mexico!
Confidential Trauma Assessment
Differences and Similarities in Stress Disorders
You have the right to feel safe, to be secure, and confident in yourself. But if you experience post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or complex post-traumatic stress disorder (CPTSD), it can make those feelings much harder to achieve.
Both PTSD and Complex PTSD are mental health conditions, found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM), that may develop after a traumatic event. It’s natural to feel overwhelmed, scared, and alone after a trauma. But if such reactions last for months or even years after the original event, it may be time to seek the guidance of mental health professionals and look for services at a facility like Icarus.
What is PTSD?

PTSD is an anxiety disorder that often develops after exposure to a traumatic event. Examples of traumatic events that someone with PTSD may have experienced include war, physical or sexual assault, a natural disaster like an earthquake or tornado, abuse as a child, and other life-threatening experiences.
Someone with PTSD may experience flashbacks and nightmares related to the event they experienced. They may also feel disconnected from their environment and have difficulty trusting other people. Other symptoms associated with PTSD include feeling extremely anxious, being easily startled, and avoiding places or things that remind them of the traumatic event.
What is CPTSD?
Complex PTSD or C-PTSD is a mental health condition that occurs when someone has gone through multiple traumas over an extended period of time. Examples of traumatic events that someone with C-PTSD may experience can include childhood abuse or neglect, sexual assault, physical violence in romantic relationships, and other types of ongoing trauma.
Those who suffer from Complex PTSD may also experience symptoms similar to those associated with PTSD such as flashbacks and nightmares related to their trauma. In addition, they may have intense feelings of guilt and shame, a fear of abandonment or betrayal, difficulty connecting to other people in meaningful ways, and an inability to regulate emotions.
How are PTSD and CPTSD Treated?
Inpatient treatment for PTSD and complex PTSD can include psychotherapy such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which is designed to help manage symptoms and thoughts related to the traumatic event. CBT can also be used to teach coping strategies for managing anxiety, fear, and other symptoms associated with PTSD or complex PTSD.
In addition, medications such as antidepressants can be prescribed to help reduce stress and improve mood. It’s important to note that these medications can take several weeks to start working, and may cause side effects like nausea, headaches, or insomnia.
Differences Between Post Traumatic Stress Disorder and Complex PTSD

You may have heard of the term Post-traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) – a mental health condition that can arise after an individual has experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. But what about Complex Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (CPTSD)? In many cases, Complex PTSD can actually be more debilitating than PTSD, and it’s important to have a clear understanding of the similarities and differences between these two disorders.
At first glance, PTSD and Complex PTSD may have some of the same symptoms – both involve suffering from distressing memories, feelings, and thoughts after an individual has been exposed to a traumatic event. However, while there are some commonalities between these two conditions, there are also some key differences that set them apart.
Type of Traumatic Event or Experience
One of the main ways that PTSD and Complex PTSD differ is in the type of trauma that an individual has experienced. With PTSD, the traumatic event is typically a single, isolated incident – such as a car accident, natural disaster, or military combat.
On the other hand, Complex PTSD is often caused by ongoing, repeated trauma – such as childhood abuse or neglect, intimate partner violence, or long-term exposure to war. In other words, the individual with C PTSD has experienced multiple traumatic events over a period of time, whereas the individual with PTSD has typically experienced only one isolated incident.
Reaction to Trauma
Another key difference between PTSD and Complex PTSD is the way in which an individual reacts to the trauma. Individuals with PTSD may have intrusive thoughts or flashbacks of the traumatic event, but they are typically able to keep these thoughts at bay during day-to-day life.
On the other hand, individuals with CPTSD often suffer from “dissociation” – a disruption in their mental processes that can cause them to disconnect from reality, or feel as though they are living in a dream-like state. This dissociation often makes it difficult for them to remember details of the trauma, which is one of the reasons why C PTSD can be particularly hard to diagnose and treat. Treatment that considers trauma, such as our offerings at Icarus, are the most effective in terms of lasting success.
CPTSD has Additional Symptoms
Individuals with PTSD may also experience a variety of PTSD symptoms, such as depression, anxiety, and difficulty sleeping. However, individuals with C PTSD often suffer from additional PTSD symptoms that can sometimes be more intense or longer lasting than those experienced by an individual with PTSD – including feelings of shame or guilt, emotional numbness and detachment, difficulty regulating emotions, and difficulty forming healthy relationships with other people.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Another key difference between PTSD and C PTSD is the way in which each of these mental health conditions is diagnosed and treated. Since PTSD is typically caused by a single traumatic event, it can often be diagnosed relatively quickly – as long as all of the diagnostic criteria are met.
C PTSD often takes longer to diagnose, since it requires a thorough evaluation of the individual’s history and current symptoms. and prolonged trauma. Additionally, treatment for complex trauma is often more intensive than treatment for PTSD – and may include trauma-focused psychotherapy, medications, or even hospitalization in some cases. The effects on a person’s life from Complex Trauma such as disability or inability to perform every day tasks, is also a determining factor in deciding the best forms of support for recovery.
What Types of Trauma Can Cause PTSD?

You may be feeling overwhelmed or confused about all the different types of past trauma that can lead to Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD is a trauma disorder). From physical abuse and violence to witnessing a traumatic event, there are many different forms of trauma that can have long-lasting effects on an individual’s mental health.
Witnessing a Life Threatening Event
The most common type of trauma that can lead to PTSD is experiencing or witnessing a life-threatening event. This could include accidents, natural disasters, war, violence, and assault. Experiencing such events can have profound psychological effects on individuals and can leave them feeling scared and vulnerable long after the initial experience has ended.
Physical Abuse
Another common form of trauma is physical abuse. This includes physical, sexual, and emotional abuse that is either experienced or witnessed. Physical abuse can occur in the home, in a school setting, or at work. Being subjected to this type of trauma can be debilitating and lead to feelings of fear and helplessness.
Other forms of trauma include psychological trauma caused by bullying or harassment, neglect, or abandonment. These experiences can lead to individuals feeling isolated and disconnected from others, resulting in feelings of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
24 Hour Trauma Treatment Hotline
Medical Trauma
Trauma from medical procedures such as surgery or childbirth can also lead to PTSD. This type of trauma is often related to the individual’s experience rather than an external event. Whether it be fear of the unknown or concern about the outcome, this type of trauma can have a lasting impact on an individual’s mental health.
Other Traumatic Events
Finally, traumatic events such as natural disasters, terrorist attacks, and mass shootings can also lead to PTSD. This type of trauma is often related to the suddenness and magnitude of the event. The aftermath of such events can be equally as traumatizing, leaving individuals feeling scared and alone.
Trauma that Causes C PTSD

Here are some of the types of trauma that someone may experience and go on to have CPTSD.
Chronic Childhood Abuse
One type of trauma is chronic childhood abuse, which includes physical and emotional abuse, along with neglect from a parent or other caregiver. Childhood abuse typically refers to recurring patterns of mistreatment over a long period of time and can have lasting psychological effects. The experience of living in a constant state of fear can lead to complex posttraumatic stress disorder.
War
Another type of trauma that can cause CPTSD is being held captive or living in a war zone. This can include being kidnapped, taken hostage, or being a refugee. If you’ve experienced any of these, you may have trouble sleeping, flashbacks, and problems with trust. Living in an environment of constant fear and danger can also lead to CPTSD.
Domestic violence
Finally, a third type of trauma that can cause CPTSD is domestic violence. This includes physical abuse, sexual assault, or psychological abuse from a partner or other family member. Ongoing domestic violence often happens over long periods of time and may even be normalized or accepted in the household. This can make it difficult to recognize and talk about the psychological effects of experiencing such trauma, which can lead to CPTSD.
Which other Mental Disorders are Mistaken for PTSD?
You may have heard of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and the effects it has on people’s lives. But there are other mental health conditions that can also be mistaken for PTSD, yet they still fall under the umbrella of trauma-related psychological conditions. Knowing the difference between these types of disorders is key to understanding how to approach mental health treatment.
The most common mental health conditions that are sometimes mistaken for PTSD include anxiety and depression, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and dissociative identity disorder (DID). These conditions can all mimic the trauma symptoms of PTSD – such as intrusive thoughts, avoidance behavior, and hypervigilance – yet they have their own unique set of characteristics that must be identified in order to provide effective treatment.
Anxiety
Anxiety is one of the most common mental disorders that are often misdiagnosed as PTSD. Anxiety is characterized by persistent fear, worry or dread over a wide range of topics or situations. People may also experience physical symptoms such as a racing heart, sweating, and difficulty breathing.
Depression

Depression, on the other hand, is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, emptiness or hopelessness. Other symptoms may include fatigue, sleep disturbances, and changes in appetite.
Borderline Personality Disorder
A bipolar personality disorder is another condition that can be mistaken for PTSD. Bipolar disorder is a mental health problem that causes extreme mood swings from manic episodes of intense energy, agitation, and euphoria to depression and extreme fatigue.
People who suffer from bipolar disorder may also experience irritability, changes in sleep patterns, and risky behavior. This condition is often misdiagnosed as PTSD due to similar symptoms such as hypervigilance and avoidance behavior.
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a mental disorder that causes intrusive thoughts, compulsive behaviors, and the need to repeatedly check or do certain tasks. People with OCD may obsess over cleanliness, orderliness, or safety.
These obsessive thoughts can lead to repetitive behaviors such as checking locks multiple times before leaving the house, washing hands excessively, or counting items. OCD can be easily mistaken for PTSD due to similar symptoms of hypervigilance, avoidance, and intrusive thoughts.
Dissociative Identity Disorder
Dissociative identity disorder (DID) is a rare mental health condition that involves the presence of multiple personalities within one person. People with DID may have memories, behaviors, or identities that are distinct from their “normal” selves.
These alternate personalities may take control of the person from time to time, leading to confusion and difficulty in distinguishing between reality and fiction. In some cases, these episodes can be mistaken for PTSD due to similar symptoms of avoidance behavior, mood swings, disorientation, and intrusive thoughts.
Get Immediate Help For Trauma and CPTSD
Get Support from the Mental Health Professionals at Icarus
Do you believe you may suffer from any of the mental health conditions talked about in this article? All of these mental health conditions can cause suffering, and they all have solutions and effective methods of treatment than can help provide relief.
If you would like to know more about getting help for PTSD, please reach out for a confidential consultation with Icarus Behavioral Health today. We accept most major insurance providers, as well as some forms of Medicaid, so call now and get options for a brighter tomorrow!